Introduction:
Today in this article we learn about Different Types of Industrial Automation Systems. Automation can generally be defined as the process of following a predetermined sequence of operations with little or no human labor, using specialized equipment and devices that perform and control manufacturing processes. Automation in its full sense, is achieved through the use of a variety of devices, sensors, actuators, techniques, and equipment that are capable of observing the manufacturing process, making decisions concerning the changes that need to be made in the operation, and controlling all aspects of it. the main three types of automation.
TYPES OF AUTOMATION :

Fixed Automation (Hard Automation):
Fixed automation refers to the use of special purpose equipment to automate a fixed sequence of processing or assembly operations. It is typically associated with high production rates and it is relatively difficult to accommodate changes in the product design. This is also called hard automation. For example, GE manufactures approximately 2 billion light bulbs per year and uses fairly specialized, high-speed automation equipment. Fixed automation makes sense only when product designs are stable and product life cycles are long. Machines used in hard-automation applications are usually built on the building block, or modular principle.
Advantages:
- Maximum efficiency.
- Low unit cost.
- Automated material handling—fast and efficient movement of parts.
- Very little waste in production.
Disadvantages:
- Large initial investment.
- Inflexible in accommodating product variety
Programmable Automation:
In programmable automation, the equipment is designed to accommodate a specific class of product changes and the processing or assembly operations can be changed by modifying the control program. It is particularly suited to “batch production,” or the manufacture of a product in medium lot sizes (generally at regular intervals). The example of this kind of automation is the CNC lathe that produces a specific product in a certain product class according to the “input program.” In programmable automation, reconfiguring the system for a new product is time consuming
because it involves reprogramming and set up for the machines, and new fixtures and tools. Examples include numerically controlled machines, industrial robots, etc.
Advantages:
- Flexibility to deal with variations and changes in product.
- Low unit cost for large batches.
Disadvantages:
- New product requires long set up time.
- High unit cost relative to fixed automation
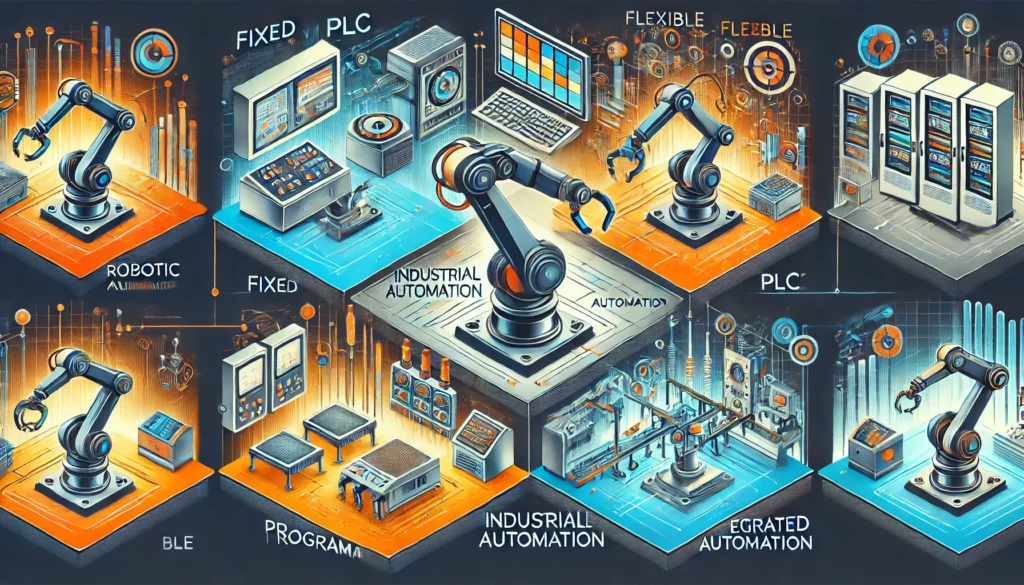
Flexible Automation (Soft Automation):
In flexible automation, the equipment is designed to manufacture a variety of products or parts and very little time is spent on changing from one product to another. Thus, a flexible manufacturing system can be used to manufacture various combinations of products according to any specified schedule. With a flexible automation system, it is possible to quickly incorporate changes in the product (which may be redesigned in reaction to changing market conditions and to consumer feedback) or to quickly introduce a new product line. For example, Honda is widely credited with using flexible automation technology to introduce 113 changes to its line of motorcycle products in the 1970s. Flexible automation gives the manufacturer the ability to produce multiple products cheaply in combination than separately.
Advantages:
- Flexibility to deal with product design variations.
- Customized products.
Disadvantages:
- Large initial investment.
- High unit cost relative to fixed or programmable automation.

Advantage of Automation:
Manufacturing companies in virtually every industry are achieving rapid increases in productivity by taking advantage of automation technologies. When one thinks of automation in manufacturing, robots usually come to mind. The automotive industry was the early adopter of robotics, using these automated machines for material handling, processing operations, and assembly and inspection. Automation can be applied to manufacturing of all types. The advantages of automation are: Increase in productivity.
- Reduction in production costs.
- Minimization of human fatigue.
- Less floor area required.
- Reduced maintenance requirements.
- Better working conditions for workers.
- Effective control over production process.
- Improvement in quality of products.
- Reduction in accidents and hence safety for workers.
- Uniform components are produced.










