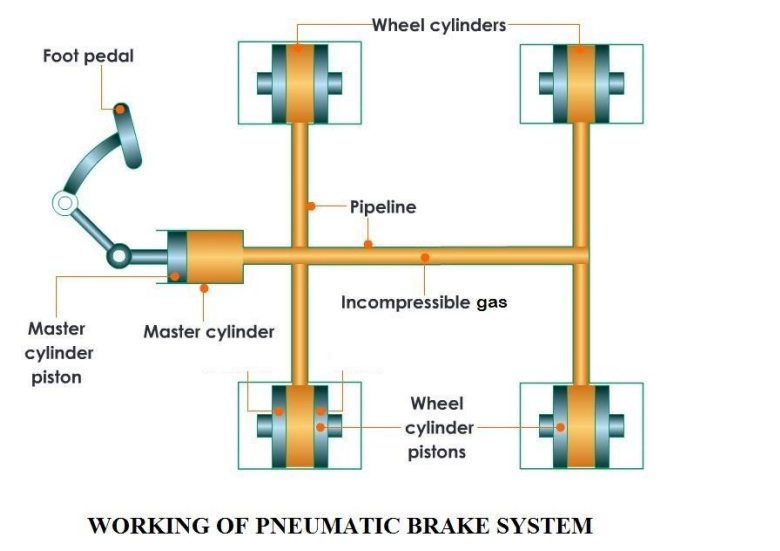
Introduction:
Today in this article we learn about what is a pneumatic system. Fluid power is an applied science dealing with ways of using pressurized gas (pneumatics) or liquid (hydraulics) for doing work. Hydraulic systems use oil, which is pumped into hydraulic cylinders or hydraulic motors and made to do work. Pneumatic systems use a pressurized air, which is directed into pneumatic cylinders and made to do work. Fluid power systems convert mechanical energy into fluid energy, and then convert this fluid energy back into mechanical energy to do useful work. The fluid power devices that convert the energy of a pressurized fluid into mechanical energy to do work, are called actuators. Most pneumatic circuits contain a source of compressed air, a pressure control device, conductors such as pipe or tubing, an actuator, and a directional control valve to control the operation of the actuator
What is pneumatic :
- In Greek “Pneuma” means air. Study (or) subject deal with “Pneuma” / compressed air is called as “Pneumatics”. Products that use compressed air as medium for operation are called as “Pneumatic components
- A pneumatic system is a system that uses compressed air to transmit and control energy. Pneumatic systems are used in controlling train doors, automatic production lines, mechanical clamps, etc.
- Pneumatic technology deals with the study of behavior’s and applications of compressed air in our daily life in general and manufacturing automation in particular.
- Pneumatic systems use air as the medium which is abundantly available and can be exhausted into the atmosphere after completion of the assigned task.
- Pneumatics started finding exhaustive industrial applications during second world war.
- Pneumatics offers a cheaper medium to achieve industrial automation
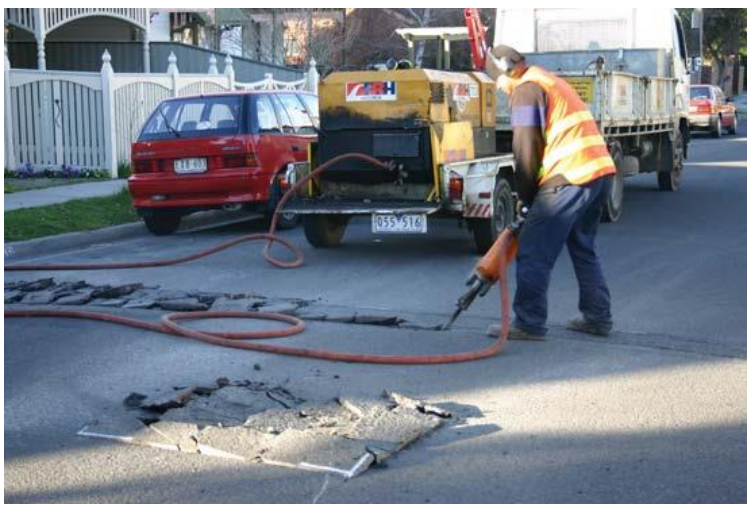
- Pneumatics, at beginning, used to find maximum application in construction industry for power tools like hammers, drills, riveting hammers etc.
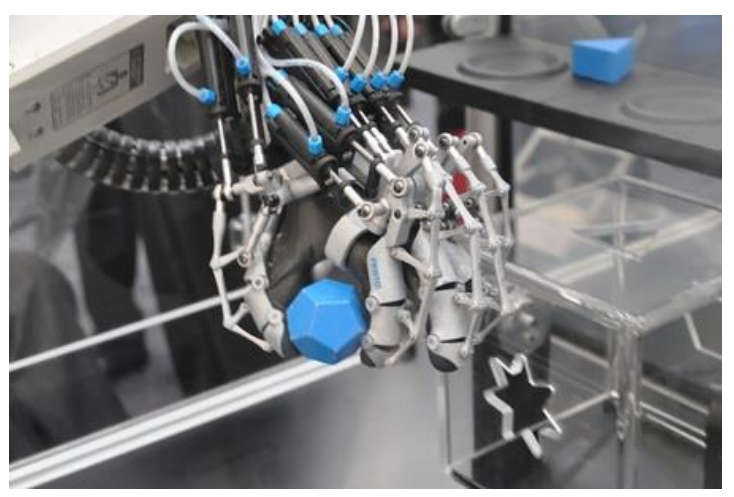
- Presently, pneumatics is heavily used in brake system in automobiles, railway coaches, wagon’s, printing presses and in robotics
Why Pneumatics?
- Wide availability of air
- Compressibility of air
- Easy transportability of compressed air in pressure vessels, containers
- and long pipes
- Fire proof characteristics of air
- Simple construction of pneumatic elements and easy handling
- High degree of controllability of pressure, speed and force
- Possibility of remote control
- Easier maintenance
- Comparatively cheaper cost
How pneumatics work:
the pneumatic system basically by work using compressed air and gas to control pneumatic energy for perform mechanical task . the pneumatic system is widely used in most industrial application such as automation, robotics, material handling, drills and pumps etc.
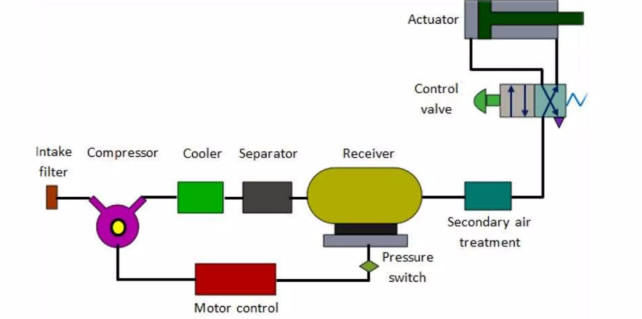
The following main components of pneumatic system:
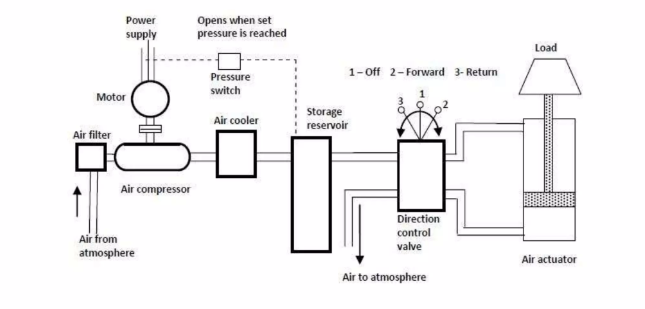
- An air tank to store a given volume of compressed air
- A compressor to compress the air that comes directly from the atmosphere . An air compressors are either diesel or electrically operated.
- An electric motor or other prime mover to drive the compressor
- Valves to control air direction, pressure, and flow rate
- Piping to carry the pressurized air from one location to another
- Air filters: To filter out the contaminants from the air.
- Air cooler: During compression operation, air temperature increases. Therefore coolers are used to reduce the temperature of the compressed air.
- Dryer: The water vapor or moisture in the air is separated from the air by using a dryer.
- Air Actuator: Air cylinders and motors are used to obtain the required movements of mechanical elements of pneumatic system.
- Electric Motor: Transforms electrical energy into mechanical energy. It is used to drive the compressor.
- Receiver tank: The compressed air coming from the compressor is stored in the air receiver.
Advantages of Pneumatic Systems:
- High Effectiveness use of compressed air in not restricted by distance & can easily be transported.
- High durability and reliability – Extremely durable and not damaged easily.
- Simple Design more suitable for use in simple automatic control systems.
- High adaptability to harsh environments compressed air is less affected by high temperature, dust, corrosion, etc.
- Safety Because they can work in inflammable environment without causing fire or explosion.
- Easy selection of speed and pressure
- Environment friendly The operation of pneumatic systems do not produce pollutants.
- Economical – The costs of pneumatic systems are quite low.
Disadvantages of Pneumatic Systems:
- Relatively low accuracy The volume of air may change when compressed or heated, the supply of air to the system may not be accurate.
- Low loading – As the cylinders of pneumatic components are not very large, a pneumatic system cannot drive loads that are too heavy.
- Processing required before use Compressed air must be processed before use to ensure the absence of water vapour or dust.
- Uneven moving speed As air can easily be compressed, the moving speeds of the pistons are relatively uneven
- Noise Noise will be produced when compressed air is released from the pneumatic components.
Comparison of Hydraulic and Pneumatics:
| Pneumatics | Hydraulic |
| Pneumatics offer a very clean system, suitable for food manufacturing processes and other processes which require no risk of contamination. | Hydraulics is generally not used in these environments due to the risk of hydraulic oil leaks from faulty valves, seals or burst hoses |
| Pneumatics offer rapid movement of cylinders and have the great advantage of availability in very small sizes. This is mainly due to air compressor flow rates, air is very agile and can flow through pipes very quickly and easily with little resistance. | While hydraulic oil is a viscous substance and requires more energy to move |
| In pneumatics, cylinders and valves can dump their compressed air straight to the atmosphere when they need to change direction or alter their state quickly | In hydraulics, the oil must be routed back to the reservoir. |
| In pneumatics, cylinders and valves can dump their compressed air straight to the atmosphere when they need to change direction or alter their state quickly | In hydraulics, the oil must be routed back to the reservoir |
| Pneumatics does not have the potential force that hydraulics has to offer. The lifting or moving of heavy loads is not best suited to pneumatics. | Hydraulics can smoothly lift and move loads because the hydraulic oil is not compressible, compared to air which can become jerky and spongy as the air pressure fluctuates with cylinder movement or load changes. In general a much larger pneumatic cylinder is needed to obtain the same force that a hydraulic ram can produce |
| Pneumatics is dealing more on studying the impact of pressurized gases and how it influences mechanical movement. | Hydraulics is used in controlling, transmitting and harnessing power using pressured fluids. |
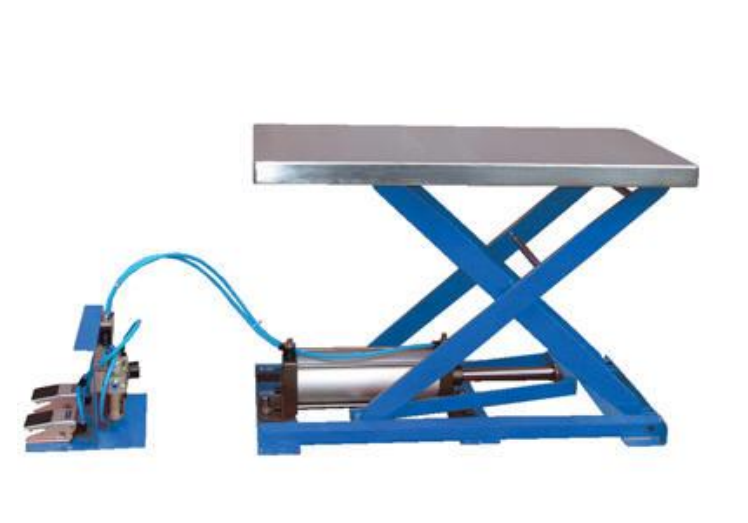
Application of Pneumatics:
Pneumatic equipment’s can be used for applications, where operation cycles need certain routine functions like
- Pushing
- Pulling
- Lifting
- Feeding
- Clamping
- Pressing
- Forming, etc.
APPLICATION AREAS:
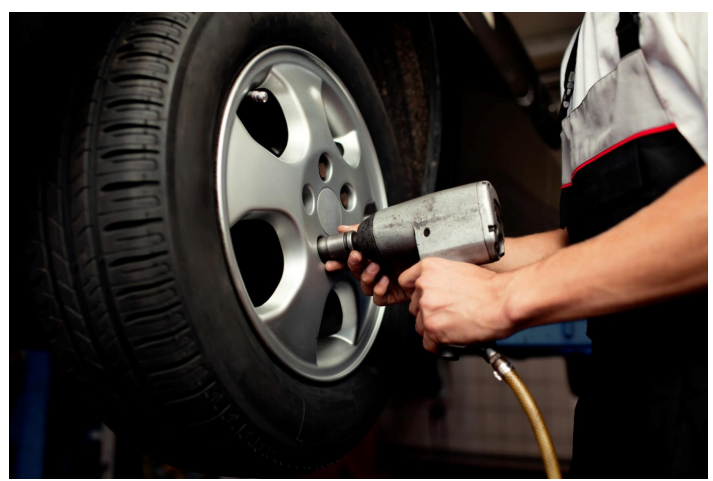
- Air brakes of automobile & trains.
- Air engine
- Pneumatic drills
- Pneumatic press, power press
- Auto motional of assembly line like automobile industry, packaging, bottling
- Pneumatic vehicle cleaning
- Anti aircraft weapon
- Pneumatic launchers
- Vacuum pump
- Pressure regulator
- Cotton mills
- Dairies
- Forge shops
- Foundries
- Metal forming
- Paper mills
- Printings